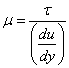Ideal fluid is incompressible and possesses no viscosity.
- Such a fluid is only an imaginary fluid.
- All existing fluids have some velocity.
A fluid that possesses viscosity is known as a real fluid.
- In actual practice, all fluids are real fluids
A real fluid in which the shear stress is directly proportional to the rate of shear strain (or velocity gradient) is called Newtonian fluid.Non – Newtonian fluids
A real fluid in which the shear stress is not proportional to the rate of shear strain (or velocity gradient) is called Non -Newtonian fluid.Ideal plastic fluid
A fluid in which the shear stress is more than the yield value and the shear stress is proportional to the rate of shear strain (or velocity gradient) is called ideal plastic fluid.