Viscosity/Dynamics viscosity
Or
Where,
 = is constant for proportionality and is known as the coefficient of dynamic viscosity
= is constant for proportionality and is known as the coefficient of dynamic viscosity
 = is called velocity gradient
= is called velocity gradient
It is defined as the property of fluid which offers resistance to the movement of one layer of fluid over another adjacent layer of the fluid.
- Two liquid layers at distance y and (y+dy) from the surface have velocity values u and (u+du)
- The top layer causes a shear stress on the adjacent lower layer while the lower layer causes a shear stress on the adjacent top layer.
- The shear stress is proportional to the rate of change of velocity with respect to y.
- Mathematically
Or
Where,
 = is constant for proportionality and is known as the coefficient of dynamic viscosity
= is constant for proportionality and is known as the coefficient of dynamic viscosity  = is called velocity gradient
= is called velocity gradient - M. K. S. unit : kgf-sec/m3
- C. G. S. unit : dyne-sec/m2 , 1 dyne-sec/m2 is called one poise
- S. I. unit : newton-sec/m2 = Ns/m2



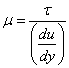



No comments:
Post a Comment